Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer Treatment in Chennai
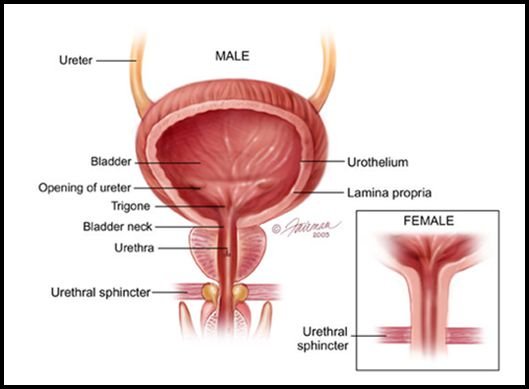
What is Bladder and Its normal Function?
Urinary Bladder or Bladder is a pear shaped structure located in the lower abdominal part which collects Urine from Kidneys before discarding by Urination. Two Ureters are connected from Kidneys to Bladder from which Urine is passed and collected in the Bladder. Urine is discarded from the Bladder through a small opening known as Urethra. In men’s Urethra longer supported by prostate gland and opens outside while in women’s Urethra is shorter and opens in front of Uterus.
What are different types of Bladder Cancer?
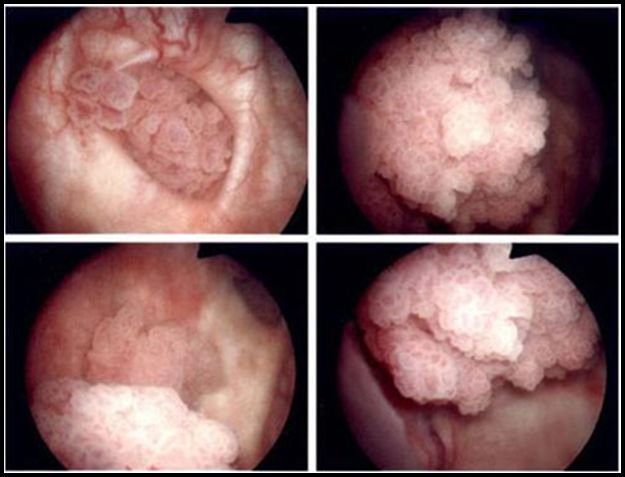
TCC: Transitional Cell Carcinoma also known as Urothelial Cell Carcinoma (UCC) is kind of Bladder Cancer seen in Urinary System; i.e. Kidney, Urinary Bladder and organs associated to it.The Cancer starting in cells i.e Transitional Epithelium, a tissue lined on the inner surface of the muffled organs and encompassing from Kidney to Bladder is known as Transitional Cell Carcinoma. If Cancer is found in Bladder Lining i.e Urothelium, it precisely denotes to TCC of the Urinary System.
Superficial Bladder Tumor: In the early stage of TCC lies only on the lining of Bladder and not deep into the layers of the Bladder Wall. Superficial Bladder Tumor appears in small growths, mushroom shaped and grows out of the Bladder Lining. These small growths can be removed and might never come back but some other kinds of non-muscle Superficial Bladder Tumor like Carcinoma in Situ (CIS) might come back which are high grade T1 Tumors
Adenocarcinoma of Bladder: This kind of Tumor starts in the cells which release mucus and other fluids and can ascend from the fragments of the Umbilical Cord. Adenocarcinoma is characterized into three bodies; Metastatic, Primary and Urachal. Adenocarcinomas which spread till bladder frequently by Direct Extension are Colon, Prostate and Tumors of Female reproductive tract. If removed completely, it can be cured. Crucial Bladder Adenocarcinomas might be Papillary, Polypoid or Nodular and affected patients are those who have long History of Cystitis and often associated with the urachus.
Causes of Bladder Cancer
- Smoking: it is a most common reason for Bladder Cancer and usually seen with men who started smoking from very young age or those who smoked for a long time. People Smoking Cigars and Pipes are also at higher risk of Bladder Cancer
- Exposure to Chemicals: People who are exposed to group of Chemicals known as Arylamines are at higher risk of Bladder Cancer. However Arylamine takes 25 years to develop as Bladder Cancer but people who are working in rubber or plastic manufacturing industries from a very long time may develop bladder cancer.
- Water Disinfections Chemicals: Exposure to THM or consumption of THM causes Bladder Cancer, Trihalomethanes or THM which is formed when Chlorine breaks down. People exposed to Chlorinated water used for drinking and swimming are at a higher risk of Bladder Cancer. Some studies have shown that Men are at higher risk of Bladder Cancer than Women while some studies show that people drinking lots of water and frequently emptying their Bladder are at lower risk of Bladder Cancer.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
- Blood While Urinating
- Blood Clots in Urine or Hematuria
- Painful Urination or Dysuria
- Urinating in Small Quantity
- Repeated Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
- Cystoscopy: Cystoscope, a narrow tube inserted through Urethra to examine the interior Urethra and Bladder. A Cystoscope has a lens and fibre-optic lighting system and done under local anesthesia or general anaesthesia.
- Biopsy: During Cystoscopy examination, a specific tool is passed through the Cystoscope to collect cell samples from Bladder for tests. This test is called as Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) and it is also used to treat Bladder Cancer and is done under general anesthesia.
- Urine Cytology: Urine samples are taken and analyzed to detect cancer cells under microscope.
- Imaging Tests: This test is to examine structures of Urinary Tract by use of dye injected into vein just before the procedure. A kind of imaging test by use of X-Ray known as Intravenous Pyelogram to highlight Kidneys, Ureters and Bladder. Computerized Tomography or CT scan helps in diagnosing and staging the disease.
Staging Bladder Cancer
Once it is confirmed for Bladder Cancer, the patient is asked for additional tests to diagnose the stage of the Bladder Cancer known as Staging Tests. CT Scan, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Bone Scan, Chest X-Ray and taken to detect the stage of Bladder Cancer.
What are the Different Stages of Bladder Cancer?
Stage 0: it is very early sign of Bladder Cancer where the tumor is found in the outermost layer of the Bladder Lining or high grade tumors are found only in the innermost layer of the bladder lining.
Stage 1: Now the tumor is seen started growing into the Connective Tissue underneath the bladder lining.
Stage 2: The tumor is seen growing over Connective Tissue layer in the muscle of the Bladder Wall.
Stage 3: The tumor is grown over the muscle into the fat layer and also spread exterior to the bladder to Prostate, Womb or Vagina.
Stage 4: The tumor is seen spreading to the Abdomen Wall, Pelvis, Lymph Nodes or other parts of the body. If it spreads to another part of the body then it is likely to grow to bones, lungs or lives.
Treatments for Bladder Cancer
Surgery: It is a part of most of the types of Bladder Cancers, the kind of surgery used for the treatment be determined by the stage of Cancer.
TURBT (Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor) is done to diagnose whether an individual has Bladder Cancer, if yes then whether the cancer has occupied the muscle layer of the bladder wall. It is a most often treatment for starting stage or superficial (non-muscle invasive) bladder cancers. Maximum patients suffer from superficial cancer at first diagnosis so generally it is their first treatment.
Intravesical Therapy: In this type of treatment for Bladder Cancer, a liquid drug is inserted through a catheter in to the bladder. This drug affects the cells lining the bladder without having any major effects on other parts of the body. Intravesical Therapy is done after TURBT for High grade non muscle invasive Bladder Cancer to prevent cancer from coming back.
There are two kinds of Intravesical Therapy, i.e Intravesical Immunotherapy and Intravesical Chemotherapy.
- Intravesical Immunotherapy: In this kind of therapy , it helps the body’s immune system to fight with cancer cells. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is the key intravesical immunotherapy for the treatment of starting stage of Bladder Cancer. BCG is the vaccine used against Tuberculosis, but it is not responsible to cause any disease. Here the BCG is inserted through catheter into the Bladder, now the body’s immune system cells infiltrate the bladder and are activated by BCG which in turn kills the cancer cells. BCG Treatment or Intravesical Immunotherapy is started after 4-6 weeks of TURBT , once there is no hematuria. Intravesical BCG is given once a week for six weeks. Even long term maintenance BCG therapy is given based on situation. Patient may have mild irritative bladder symptoms, if severe enough need to see his doctor immediately.
- Intravesical Chemotherapy: In this therapy chemotherapeutic drugs are inserted through catheter into the Bladder, it kills the vigorously growing cancer cells. The Chemo Drugs can also be given systemically i.e generally injecting into the vein for the treatment of more advanced stages of Bladder Cancer.
Radical Cystectomy : In cases of localized muscle-invasive bladder cancer, the bladder is removed surgically which can be done by Open/ Laparoscopic / Robotic technique. Either a Neobladder is made from a part of the small intestine which may require postoperative CIC, Bladder wash and very good patient compliance or a urinary diversion in the form of ileal conduit is made in which a loop of small bowel connected with the ureter is brought out through the abdominal wall and the urine is collected in an external bag. It is usually easier to manage but the patient has to carry a life long bag on his abdomen.

Chemotherapy: Use of Chemo Drugs to treat Cancer is known as Chemotherapy, Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer can be done in two different ways i.e Intravesical Chemotherapy and Systemic Chemotherapy
- Intravesical Chemotherapy: Insertion of Chemo Drug into the Bladder with the use of Catheter and used in starting stages of Bladder Cancer to kill the active growing cancer cells. Can also be injected into the vein in advanced stages of Bladder Cancer.
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Chemo Drugs prescribed in the form of medicines or injected into a vein (IV) or muscle (IM), chemo drugs travel throughout the body in blood stream this is known as Systemic Chemotherapy. This kind of Chemotherapy affects the cancer cells to the great extent from the mains tumor.
Chemotherapy is done before the surgery to downstage the tumor and for easy removal if a local spread is suspected. Chemotherapy done before surgery is called as Neoadjuvant Therapy and if done after surgery Adjuvant Therapy.
Radiation Therapy: In this kind of therapy high energy radiations are given to kill the cancer cells. Radiations are given on external part of body hence known as External Beam Radiation Therapy, before the treatment proper measurements are taken for correct angles to aim the radiation beams and for proper dosage of radiation. This is known as Simulation Session which includes CT Scan or MRI Scan, Radiation Therapy is done five days in a week on several weeks treatment.
Radiation Therapy is done when treating starting stages of Bladder Cancer, usually after surgery where the bladder is not removed completely such as TURBT. Radiation Therapy can be done for patients who are incapable to have surgery.
