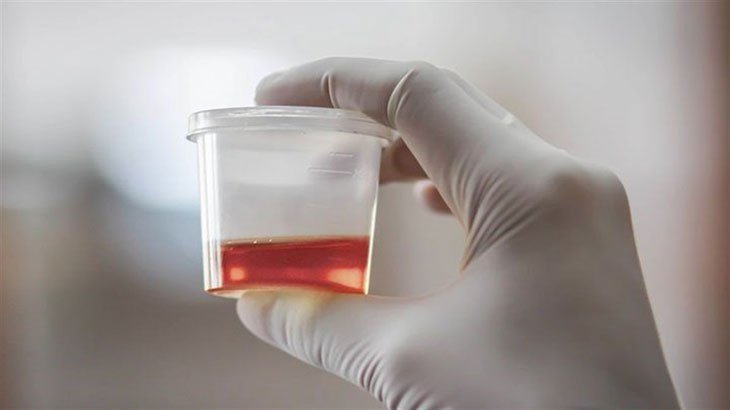
Finding blood in your urine, a condition known as hematuria, can be alarming. While it can sometimes indicate a serious medical issue, there are also many benign causes. Understanding the potential reasons behind hematuria, how it’s diagnosed, and the treatment options available is crucial for maintaining your health and peace of mind. This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of hematuria to help you stay informed and proactive about your health.
Types of Hematuria
- Gross Hematuria Gross hematuria is when you can see blood in your urine with the naked eye. The urine may appear pink, red, or cola-colored due to the presence of red blood cells.
- Microscopic Hematuria Microscopic hematuria is when blood in the urine is not visible to the naked eye but can be detected under a microscope. This type is often discovered during routine urine tests.
Common Causes of Hematuria
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) UTIs can cause inflammation and irritation in the urinary tract, leading to the presence of blood in the urine. Symptoms may include a strong urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
- Kidney Stones Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that can form in the kidneys. As they pass through the urinary tract, they can cause bleeding, leading to hematuria. Symptoms often include severe pain in the side and back, nausea, and vomiting.
- Bladder or Kidney Infections Infections in the bladder (cystitis) or kidneys (pyelonephritis) can cause hematuria. Other symptoms may include fever, chills, and pain in the lower abdomen or back.
- Enlarged Prostate In men, an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) can press on the urethra, causing difficulty urinating and sometimes blood in the urine.
- Cancer Hematuria can sometimes be a sign of bladder, kidney, or prostate cancer. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, so it’s important to seek medical advice if you notice blood in your urine.
- Inherited Disorders Some genetic conditions, such as Alport syndrome and sickle cell anemia, can cause blood in the urine.
- Medications Certain medications, like blood thinners (anticoagulants) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can cause hematuria as a side effect.
- Strenuous Exercise Intense exercise can sometimes cause hematuria, a condition known as “runner’s hematuria.” This is usually harmless and resolves on its own with rest.
Diagnosis of Hematuria
If you notice blood in your urine, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. They may conduct several tests to determine the cause, including:
- Urinalysis: A urine sample is examined for the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, and other substances.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the urinary tract and identify any abnormalities.
- Cystoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera (cystoscope) is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to inspect the bladder and urethra for any issues.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify signs of kidney disease or other underlying conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hematuria depends on the underlying cause:
- Antibiotics: If a UTI or other bacterial infection is causing the hematuria, antibiotics can clear the infection.
- Medication Adjustments: If medications are causing hematuria, your doctor may adjust your dosage or prescribe an alternative.
- Lifestyle Changes: Drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding strenuous exercise, and following a healthy diet can help manage and prevent hematuria.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where kidney stones or tumors are causing hematuria, surgical procedures may be necessary.
Preventing Hematuria
While not all cases of hematuria can be prevented, some lifestyle changes can reduce your risk:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help flush out your urinary tract.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintain proper hygiene to prevent infections.
- Avoid Strenuous Exercise: Moderating exercise intensity can help prevent exercise-induced hematuria.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups can help detect and address potential issues early.
Conclusion
Hematuria can be a concerning symptom, but understanding its potential causes and seeking prompt medical advice can lead to effective treatment and peace of mind. If you notice blood in your urine, don’t ignore it. Consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate treatment. Staying informed and proactive about your health is the best way to ensure your well-being.