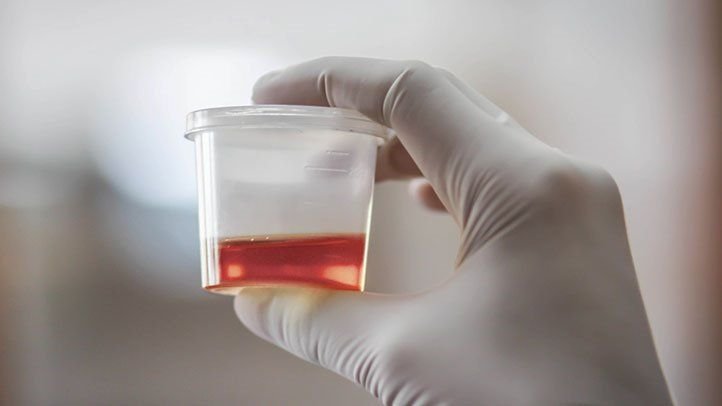
Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, is a medical condition that can be alarming to discover. While it can sometimes be a sign of a serious underlying issue, it can also result from less severe causes. This blog aims to shed light on what hematuria is, its potential causes, symptoms to watch out for, and the treatment options available.
What is Hematuria?
Hematuria refers to the presence of red blood cells in the urine. It is classified into two types:
- Gross Hematuria: This is when blood is visible to the naked eye. The urine may appear pink, red, or cola-colored due to the presence of blood.
- Microscopic Hematuria: This is when blood is not visible and can only be detected under a microscope. It is usually found during routine urine tests.
Causes of Hematuria
Hematuria can have many causes, ranging from benign to serious. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are one of the most common causes of hematuria. Bacteria can enter the urinary tract and cause inflammation, leading to blood in the urine. Symptoms often include a strong urge to urinate, a burning sensation while urinating, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
2. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys. They can cause severe pain and may lead to hematuria when they irritate or damage the urinary tract as they pass through.
3. Bladder or Kidney Infections
Infections in the bladder (cystitis) or kidneys (pyelonephritis) can cause hematuria. These infections might also present with fever, back or abdominal pain, and frequent urination.
4. Strenuous Exercise
Intense exercise, particularly high-impact activities, can cause temporary hematuria. This is usually benign and resolves on its own. However, persistent hematuria after exercise should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
5. Medications
Certain medications, like anticoagulants (blood thinners), aspirin, and some antibiotics, can cause hematuria as a side effect.
6. Kidney Disease
Various kidney diseases, such as glomerulonephritis or polycystic kidney disease, can cause blood in the urine. These conditions often require more comprehensive medical management.
7. Cancer
Hematuria can sometimes be a sign of cancer in the urinary tract, including bladder, kidney, or prostate cancer. It is essential to investigate this symptom thoroughly to rule out malignancy.
8. Inherited Disorders
Certain genetic conditions, like Alport syndrome and sickle cell anemia, can cause blood in the urine.
Symptoms Associated with Hematuria
The primary symptom of hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine, but this can come with other symptoms depending on the underlying cause. These may include:
- Painful urination
- Frequent urination
- Abdominal or back pain
- Fever and chills (in case of infections)
- Nausea and vomiting (especially with kidney stones)
Diagnosing Hematuria
To diagnose the cause of hematuria, a healthcare provider may perform the following tests:
- Urinalysis: To check for the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, and other substances in the urine.
- Urine Culture: To detect any bacterial infections.
- Blood Tests: To assess kidney function and look for signs of underlying conditions.
- Imaging Tests: Such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the urinary tract.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder to look for abnormalities.
Treatment Options
The treatment for hematuria depends on the underlying cause:
- Antibiotics: For UTIs or other bacterial infections.
- Increased Fluid Intake: To help flush out kidney stones or infections.
- Medications: To manage conditions like kidney disease or to reduce inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Including adjustments in diet and exercise to prevent kidney stones.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases of severe kidney stones, tumors, or other structural issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While hematuria can be benign, it is important to seek medical attention if you notice blood in your urine. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and address potentially serious underlying conditions.
Key Takeaways
Hematuria is a symptom that should never be ignored. Understanding its potential causes, recognizing associated symptoms, and seeking timely medical evaluation can ensure appropriate treatment and better health outcomes. If you experience blood in your urine, consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and receive the necessary care.
Stay informed, and take proactive steps towards maintaining your urinary tract health.