Prostate
Prostate
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement is a common medical condition as men grow older. The condition can lead to annoying urinary symptoms. If left untreated, BPH has the potential of blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder and causing urinary tract, bladder or kidney problems
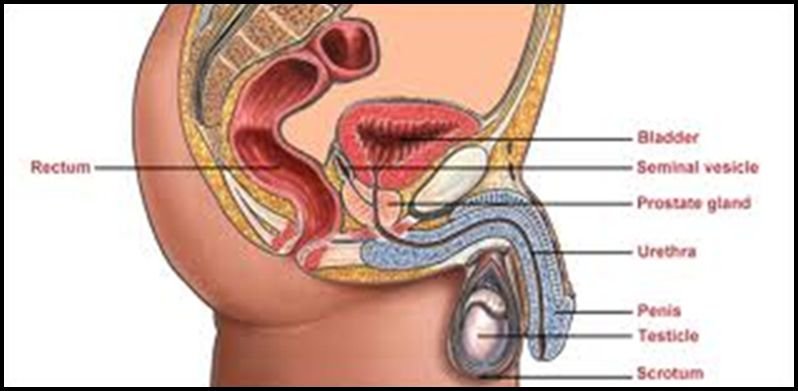
The Prostate is a small walnut-sized gland that sits just beneath a mans bladder and produces the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Urethra is a tube that carries urine out of your body from the bladder out of your penis. It passes through the middle of the prostate. When the prostate enlargement occurs, it begins to block urine flow.
Diagram of Prostate
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is not the same as prostate cancer and does not affect a man’s ability to father children it is a common condition in men over the age of 50.
What causes BPH?
What causes the prostate gland to enlarge is not clear. However, according to experts, the condition might be due to changes in the male sex hormones as men age. Those who have a family history of BPH are at increased risk to develop the symptoms.
What are the Symptoms of BPH?
The symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia are often very mild at first, but they tend to gradually become more serious if they aren’t treated. Common signs and symptoms include.
- Urgent or frequent urge to urinate
- Difficulty urinating
- Nocturia which is increased frequency of urination at night
- Weak urine stream
- Not able to empty the bladder completely
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Pus in the urine
- Straining during urination (dysuria)
- Blood in the urine
How is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Doctor may be able to diagnose BPH by taking a medical history and performing a physical examination which includes rectal exam (urinalysis), urine test and blood test. If your doctor suspects there’s an underlying cause to your condition, he or she will perform various tests. Tests may include:
- Urinalysis looks for blood and bacteria in your urine.
- Urinary flow test
- Postvoid residual volume test: A post-void residual is done to measure how much urine is left in the bladder after you urinate.
- Transrectal ultrasound
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test: This is a blood test used to check for cancer of the prostate
- Prostate biopsy: in this test a small amount of prostate tissue is removed and examined for abnormalities.
- Cystoscopy: During a cystoscopy a small tube fitted with a camera is inserted into the body to view the inside of the urethra and bladder
- Intravenous pyelogram or CT urogram
What are the Treatments for BPH?
There are various treatments for Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), including medications, surgery and minimally invasive therapies. What prostate gland enlargement treatment options are available to you depend on several factors, such as symptoms, the size of prostate, other health conditions and your preferences.
For some men, symptoms subside through self-care. If it does not happen, the doctor will determine which medication is right for you.
Prescription Medications
There are a number of medical treatments that can be used to treat BPH. Prescription treatments to help treat BPH include:
- Alpha blockers: Alpha-1 blockers are medications that relax the bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers making it easier for urine to flow. Examples of alpha-1 blockers include alfuzosin, tamsulosin , silodosin.
- Combination drug therapy: Alpha blocker with Anti 5 reductase inhibitor (Dutasteride or Finasteride)
Surgery for BPH
There are various types of surgical therapy.
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP):
The most common surgical treatment for BPH, Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) involves the insertion of a lighted scope through your urethra into the prostate. the surgeon removes the prostate piece by piece.
Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP):
This procedure is same as TURP. However the prostate gland isn’t removed. On the contrary, the surgeon makes one or two small incision in the prostate. This allows urine to flow more freely. Usually done for very small gland with High standing bladder neck.
LASER
Holmium, Thulium and KTP ( Green Light) are used either to vaporize or enucleate the prostate.
